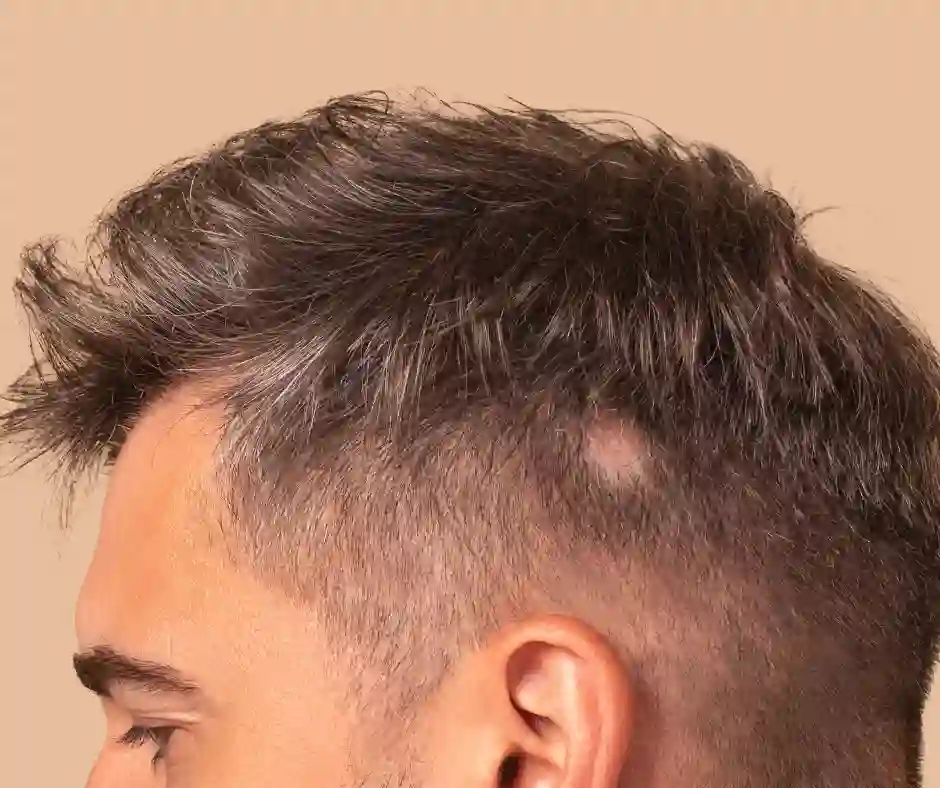
If you’ve ever asked yourself, “Why is my hair falling out?” or “Why do I lose my hair?,” you’re not alone. Millions of people around the world struggle with hair loss, and one of the most common autoimmune causes is Alopecia Areata. This condition can affect men, women, and even children, often appearing suddenly and unexpectedly. Understanding what is Alopecia Areata, its triggers, and treatment options is the first step toward managing it effectively.
In this article, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and risk factors of Alopecia Areata, along with available treatments and practical strategies to restore confidence. Whether you’re looking for answers about alopecia areata in women or curious about the best therapies, this guide will provide a comprehensive overview.
Understanding Alopecia Areata
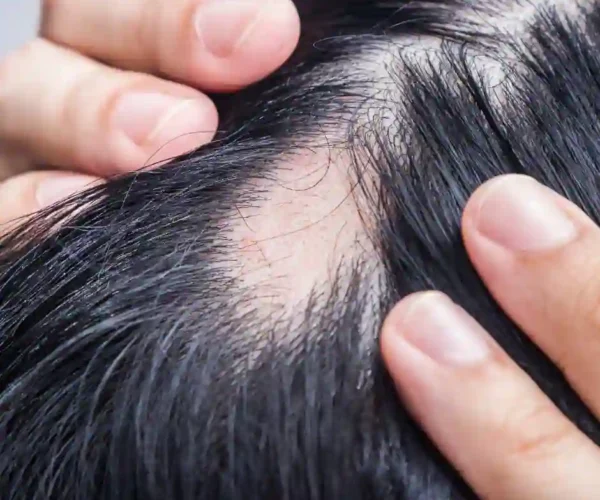
Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes the body’s immune system to mistakenly attack hair follicles. This leads to sudden hair loss in small, round patches, typically on the scalp, but it can also affect eyebrows, eyelashes, and other body hair.
The severity of Alopecia Areata varies widely. Some people may only develop a few patches, while others may experience more widespread hair loss. In rare cases, it can progress to Alopecia Totalis (complete scalp hair loss) or Alopecia Universalis (loss of all body hair).
If you’ve been asking, “What is Alopecia Areata?” or wondering, “Can stress cause hair loss?,” you’re already exploring one of the most important aspects of this condition—its connection to both immune function and lifestyle factors.
Causes of Alopecia Areata
The exact cause of Alopecia Areata remains unknown, but research suggests it is an autoimmune response triggered by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors.
1. Autoimmune Reaction
Alopecia Areata occurs when the immune system mistakenly targets healthy hair follicles, disrupting the hair growth cycle and leading to hair loss. This immune dysfunction is the primary cause of the condition.
2. Genetic Predisposition
People with a family history of autoimmune diseases such as thyroid disease, vitiligo, or lupus may have a higher risk of developing Alopecia Areata. Genetics play a significant role in determining who is more likely to experience this type of hair loss.
3. Stress and Emotional Triggers
Many patients ask, “Can stress cause hair loss?” The answer is yes—stress is known to exacerbate autoimmune conditions, including Alopecia Areata. While stress may not directly cause the disease, it can trigger flare-ups or worsen existing symptoms.
4. Environmental Factors
Environmental influences such as viral infections, exposure to toxins, or sudden lifestyle changes can contribute to the onset of Alopecia Areata.
Symptoms of Alopecia Areata
Recognizing the signs early can help with quicker alopecia areata diagnosis and more effective treatment. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden hair loss in small, round patches on the scalp or body.
- Exclamation point hairs (short, broken hairs that taper at the base).
- Thinning or shedding of hair in a short period.
- Changes in nails, such as pitting or ridging.
Hair loss can be unpredictable—patches may regrow and fall out again, making the condition frustrating and emotionally challenging. For alopecia areata in women, the impact on self-confidence is often significant, given the societal importance placed on hair.
Risk Factors of Alopecia Areata
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing Alopecia Areata:
- Family history of autoimmune diseases.
- Personal history of conditions such as thyroid disorders or vitiligo.
- High stress levels or recent traumatic experiences.
- Age—though it can occur at any time, it often begins before age 30.
Understanding these risk factors can support more proactive alopecia areata diagnosis and management.
How is Alopecia Areata Diagnosed?
A dermatologist typically performs an alopecia areata diagnosis by examining the pattern of hair loss and reviewing medical history. In some cases, a scalp biopsy or blood tests may be recommended to rule out other autoimmune conditions or confirm the diagnosis.
Early diagnosis is crucial to developing a personalized alopecia areata treatment plan and preventing further progression.
Treatment Options for Alopecia Areata
While there is no absolute cure, several effective alopecia areata treatments exist that can help regrow hair and reduce flare-ups. Treatment is tailored to each individual’s severity and response.
1. Corticosteroid Injections
These anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly used to suppress immune activity at the hair follicle. They are effective for small patches of hair loss.
2. Topical Medications
Topical corticosteroids, minoxidil, or immunotherapy creams can stimulate regrowth and support follicle health.
3. Oral Medications
In severe cases, oral immunosuppressants may be prescribed to reduce autoimmune activity. However, these come with potential side effects and require close monitoring.
4. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves using your own blood plasma, rich in growth factors, to stimulate hair follicles. This has gained popularity as a promising alopecia areata treatment, especially when combined with other therapies.
5. Lifestyle Modifications
Since stress plays a major role, stress management techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, and proper sleep hygiene can help reduce hair loss triggers.
Alopecia Areata in Women: Unique Challenges
Alopecia areata in women often has a profound psychological impact due to cultural expectations surrounding female beauty and hair. Many women experience anxiety, depression, or social withdrawal. Treatment plans for women should incorporate not only medical solutions but also emotional support and counseling.
Women are also more likely to explore cosmetic solutions, such as wigs, scalp micropigmentation, or cosmetic fillers, alongside alopecia areata treatments for long-term results.
Lifestyle Tips to Manage Alopecia Areata
- Eat a nutrient-rich diet with vitamins that support hair growth (Biotin, Vitamin D, Zinc).
- Practice regular stress management activities.
- Avoid harsh chemical treatments on hair.
- Stay consistent with medical treatments and follow-up appointments.
While asking “Why do I lose my hair?” can feel overwhelming, these small lifestyle shifts can help improve overall hair health and support ongoing treatments.
External Source
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, Alopecia Areata is one of the most common autoimmune hair loss conditions, affecting nearly 2% of people at some point in their lives.
Alopecia Areata Treatment at Par Par Aesthetics
If you are struggling with Alopecia Areata and searching for effective solutions, Par Par Aesthetics offers personalized Alopecia Areata Treatment in Airmont, NY. Our team provides advanced therapies, including PRP and other non-surgical treatments, designed to restore hair growth and confidence. Every treatment plan is tailored to your unique needs, ensuring comfort, safety, and visible results.
Conclusion
Hair loss is never easy to face, but understanding what is Alopecia Areata, why it happens, and what treatments are available can make the journey much more manageable. If you’ve been wondering, “Why is my hair falling out?” or “Can stress cause hair loss?,” it’s time to take action. With early diagnosis, personalized alopecia areata treatment, and supportive care, you can regain control of your hair health and confidence.